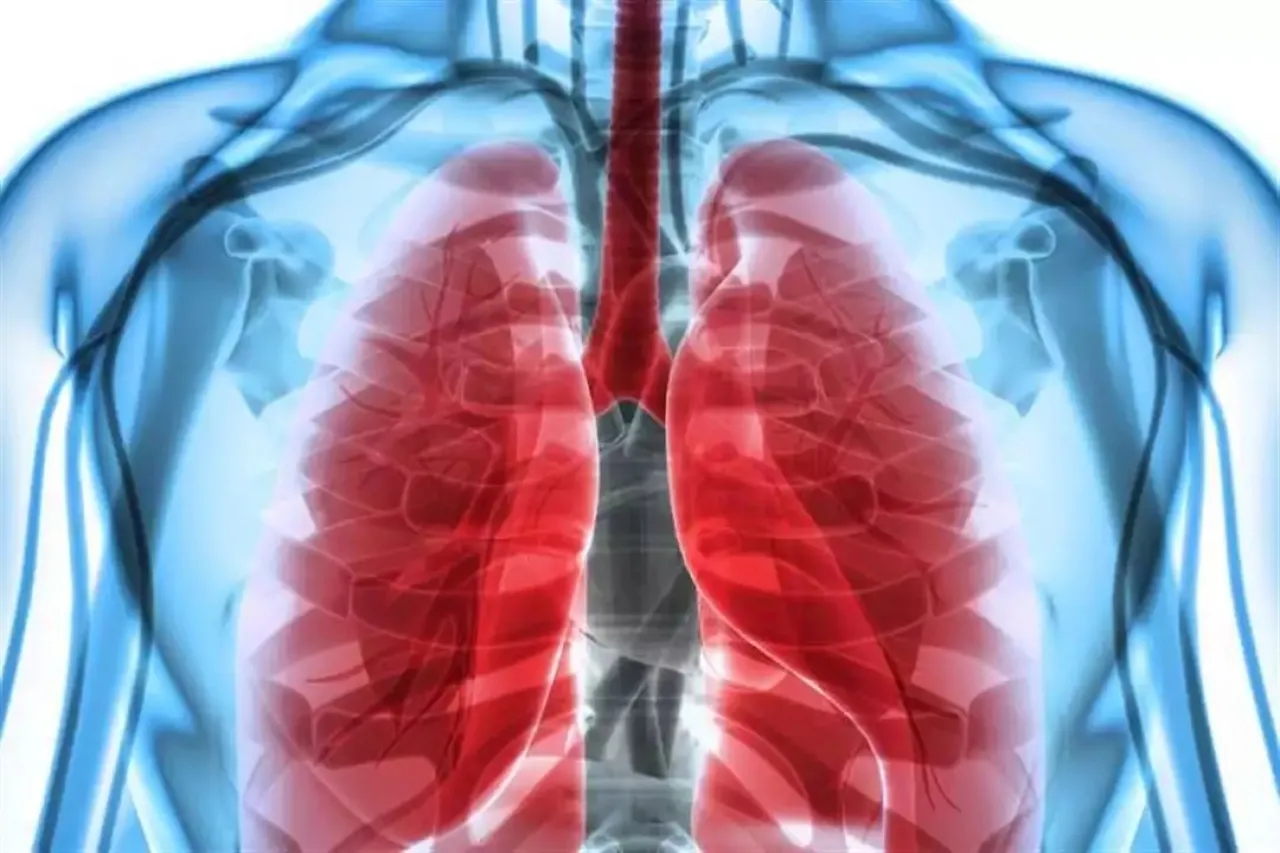
Khaberni - The World Health Organization announces that pneumonia is a serious lung infection targeting children under the age of five worldwide. The disease leads to the alveoli being filled with pus or fluids, which obstructs oxygen exchange and affects breathing. Approximately 30 million children under the age of five are infected, with fatalities reaching about 14% of those infected.
Bacteria and viruses are the main causes of pneumonia, and fungi are rarely the cause. When pneumonia spreads throughout the body, it weakens the lungs and the immune system in general. Early detection and recognising the signs in children are key to prevention.
Main signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of pneumonia in children are consistent, including persistent cough, whether accompanied by phlegm or not. It is often accompanied by rapid breathing which increases as fluid accumulates in the lungs, and there may be noticeable skin tightening between the ribs or widening of the nostrils during breathing. Some children suffer from pain or discomfort in the chest area, making breathing more difficult.
Fevers accompanied by chills indicate the presence of an infection; a fever higher than 38.5 degrees Celsius with chills is an indicator of a more serious infection that requires immediate medical attention. Some children complain of extreme fatigue and weakness and a decline in daily activity, reflecting the impact of pneumonia on the body. Appetite loss can decrease food intake, which hampers the provision of energy needed to fight the infection.
Severe indicators such as blueness of the lips or nails are signs of oxygen deficiency and expansion of the infection into the chest cavity, necessitating immediate medical care. If signs of breathing difficulties or persistent blueness appear, urgent medical help is needed. Also, the presence of severe fever or severe symptoms in infants requires swift medical care.
When to seek medical help?
Medical assistance should be sought immediately if the child experiences difficulty breathing or a continuous high fever. In such cases, quick response can protect against worsening conditions and reduce the risks of complications. Parents should direct the child to healthcare services if symptoms persist or worsen within a few days of starting home treatment.
Prevention and care methods
Calls for protecting children under the age of five through vaccination with the pneumococcal vaccine and the Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccine. It also emphasizes the importance of providing a balanced diet that supports natural immunity in children. Managing the home environment by reducing indoor air pollution and avoiding smoking lowers the risk of infection and speeds up recovery. It also stresses maintaining personal hygiene practices such as hand washing and avoiding smoking in enclosed and open spaces.