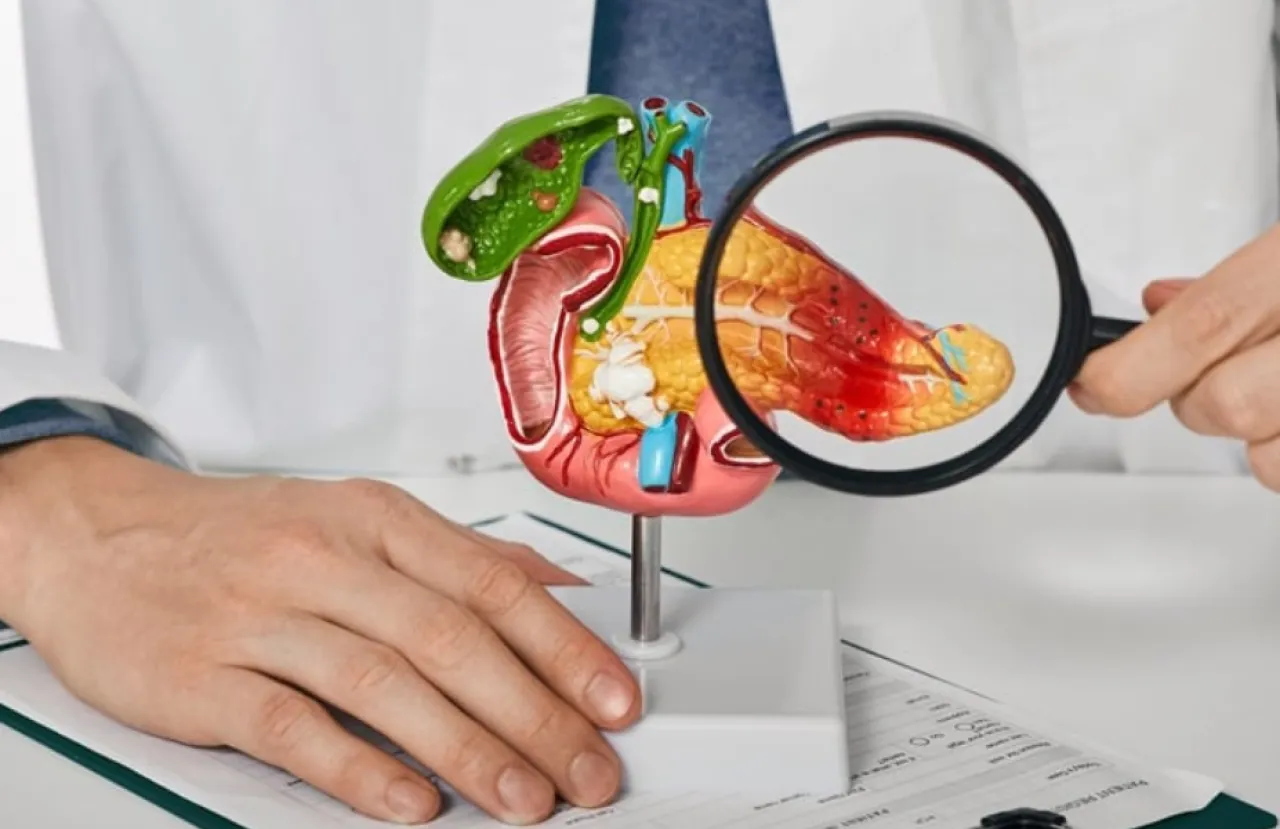
Khaberni - The pancreas is an essential organ for survival and good health. This small organ, located behind the stomach, has two main functions: it produces digestive enzymes that break down food, and hormones such as insulin and glucagon that regulate blood sugar.
Unhealthy daily habits can gradually damage the pancreas. Once it is damaged, the consequences can be severe, including inflammation, diabetes, and in some cases, cancer.
According to "Medical Express," there are habits that stress the pancreas:
1. Smoking
Smoking increases the risk of acute and chronic pancreatitis. Acute pancreatitis develops suddenly with severe pain and nausea. This inflammation develops over many years.
Numerous studies indicate that the more smoking increases, the greater the risks. One study found that quitting smoking significantly reduces the risks, and about 15 years after quitting, the risk can decrease to nearly that of a non-smoker.
Scientists do not yet fully understand the mechanism of how smoking is linked to the pancreas, but laboratory studies show that nicotine stimulates sudden increases in calcium inside pancreatic cells, and tobacco smoke also contains carcinogenic substances that damage DNA.
2. Diet
Diet affects the pancreas in many ways. Eating too much saturated fat, processed meats, and refined carbohydrates increases the risk of pancreatic problems.
Gallstones are one of the main causes of acute pancreatitis.
Gallstones may block the bile duct and trap digestive enzymes inside the pancreas, and when these enzymes accumulate, they begin to damage the organ.
The diet contributes to the formation of gallstones because high cholesterol levels make bile more prone to forming stones.
Also, high triglyceride levels contribute to blocking the tiny blood vessels in the pancreas. This reduces the oxygen supply and stimulates the release of harmful fatty acids that irritate the pancreatic tissues.
On the other hand, repeated spikes in blood sugar from sugary foods stress the pancreas.
Constant increases in insulin reduce insulin sensitivity and may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer.
3. Obesity
Obesity increases the risk of acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer.
Fat can accumulate in and around the pancreas, a condition called fatty pancreas disease or non-alcoholic fatty pancreatic disease, which can replace healthy cells and weaken the organ.
4. Physical inactivity
A sedentary lifestyle exacerbates insulin resistance and forces the pancreas to produce more insulin.
Without activity to help muscles absorb glucose, the pancreas remains under constant pressure. This metabolic stress increases the likelihood of diabetes and pancreatic cancer.
Physical activity directly and indirectly reduces the risk of pancreatic cancer. It supports immune function, improves cell health, and regular movement strengthens the body's antioxidant defenses.
Health guidelines recommend practicing strength exercises at least twice a week and aiming for 150 minutes of moderate activity, or 75 minutes of vigorous activity weekly.