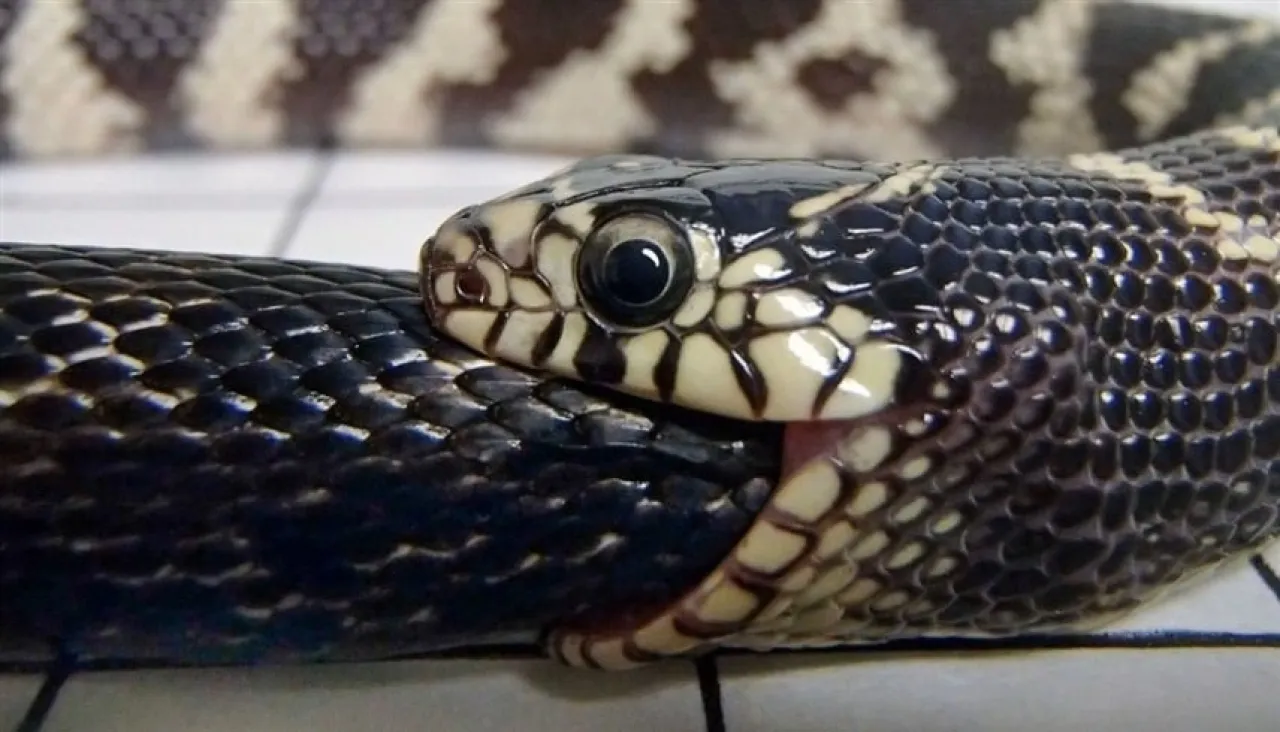
Khaberni - A recent study indicated that snakes eating each other's meat is not a rare phenomenon, but has independently developed at least 11 times throughout the evolutionary history of snakes, which amazes scientists and reveals unconventional survival strategies in the animal kingdom.
The researchers reviewed more than 500 scientific reports on this behavior among 207 species of snakes across all continents, either in the wild or in captivity, and concluded that this behavior often appears under conditions of environmental stress or limited food resources, which seems to grant snakes the ability to adapt and survive, according to the website "Life Science".
Opportunistic behavior and not just a peculiarity
As for her part, Bruna Falcao, a graduate student at the University of São Paulo and the lead author of the study, said: "For humans, eating meat of the same species seems disgusting, but for snakes, it is a useful way to maintain their environmental balance... It's a strategic choice."
The study suggests that the behavior of eating meat of the same species resembles what is observed in some spiders and the praying mantis during mating, where this practice might help in controlling the size of the clutch or overcoming food scarcity.
Most common focus centers
The analysis showed that this behavior is particularly widespread among the families of snakes "Colubridae", "Viperidae", and "Elapidae". For instance, the first family accounted for about 29% of all cases, while the second recorded about 21%, most of them in captivity where tightness and limited food augment the likelihood of this behavior. As for the third family of venomous snakes, including cobras, it accounted for about 19% of the cases, which is expected given their opportunistic behavior in the wild.
Dietary flexibility and selective behavior
The researchers found that about half of the snake species that eat meat of their own kind feed on multiple types of food, reflecting their ability to adapt to different conditions. However, the jaw's ability to accommodate prey of the same size is considered an essential factor for the evolution of this behavior in some species.
What is the significance of this study?
Xavier Glouadas, a biologist with National Geographic says: "Most reports of snakes eating their own kind were undocumented, and this study provides a comprehensive view that helps us understand the environmental and adaptive factors behind this behavior"
The study pointed out that the behavior of snakes eating meat of their own kind is not only a response to environmental pressure but also reflects these reptiles' opportunistic adaptability to their conditions, which makes them one of the most successful branches in the tree of life, existing in all continents except Antarctica.