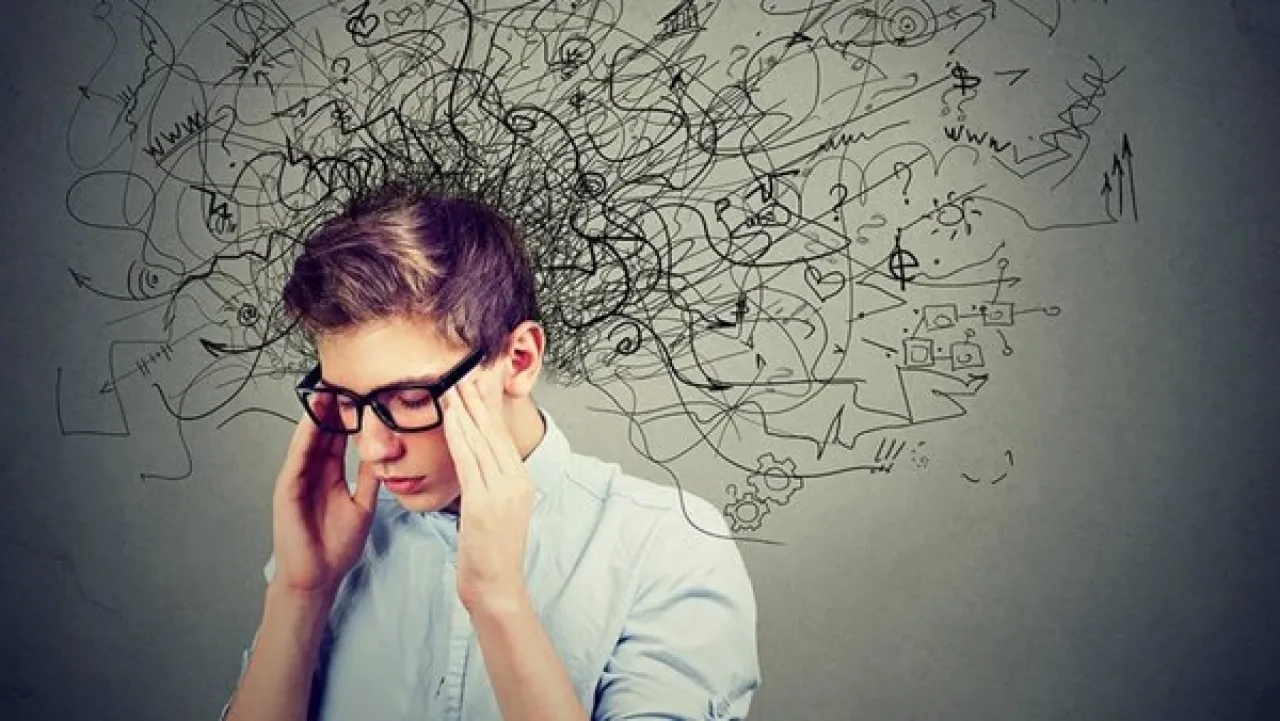
Khaberni - Catastrophic thinking is a common pattern of thought where the worst possible outcomes of any situation are imagined, even if these outcomes are highly unlikely. While experts say that normal anxiety is natural, catastrophic thinking can turn minor fears into severe anxiety; negatively affecting mental health.
According to experts from the priorygroup website focused on mental health, the effect of catastrophic thinking is like a "snowball," where simple fears quickly grow into a full-blown mental crisis. For example, if a loved one is late returning home, a person may quickly go from mild worry to imagining serious harm or death.
Studies indicate that catastrophic thinking is linked to several psychological disorders, including anxiety disorders, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Research also shows that people who engage in catastrophic thinking are more susceptible to developing symptoms of anxiety and psychological trauma, especially after difficult experiences or traumas.
What causes catastrophic thinking?
There is no single cause of catastrophic thinking. Experts suggest that it often develops as an acquired reaction associated with childhood experiences, trauma, or chronic stress. For some people, imagining the worst scenarios can provide a false sense of control or protection from disappointment. The biological makeup of the brain also plays a role, as it naturally focuses on threats due to the survival "fight or flight" response.
There are certain personality traits and circumstances that increase the likelihood of catastrophic thinking, such as perfectionism, persistent negative thinking, and situations characterized by uncertainty or loss of control. Over time, this pattern can impact work, relationships, physical health, and daily tasks.
What is the solution?
Mental health experts recommend several strategies that can be practiced daily to reduce catastrophic thinking. Mindfulness techniques and focusing on the present, and "thought-stopping" techniques, can help interrupt negative thoughts and shift attention. Healthy habits such as regular exercise, getting adequate sleep, and eating a balanced diet also play an important role in managing stress.
For individuals who experience severe or persistent catastrophic thinking, professional therapy may be necessary. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective methods, helping individuals recognize and challenge harmful thought patterns. In some cases, medication may be prescribed if catastrophic thinking is linked to an underlying psychological condition.
In conclusion, experts affirm that support is available, and learning to manage catastrophic thinking can improve the quality of life and increase psychological resilience.