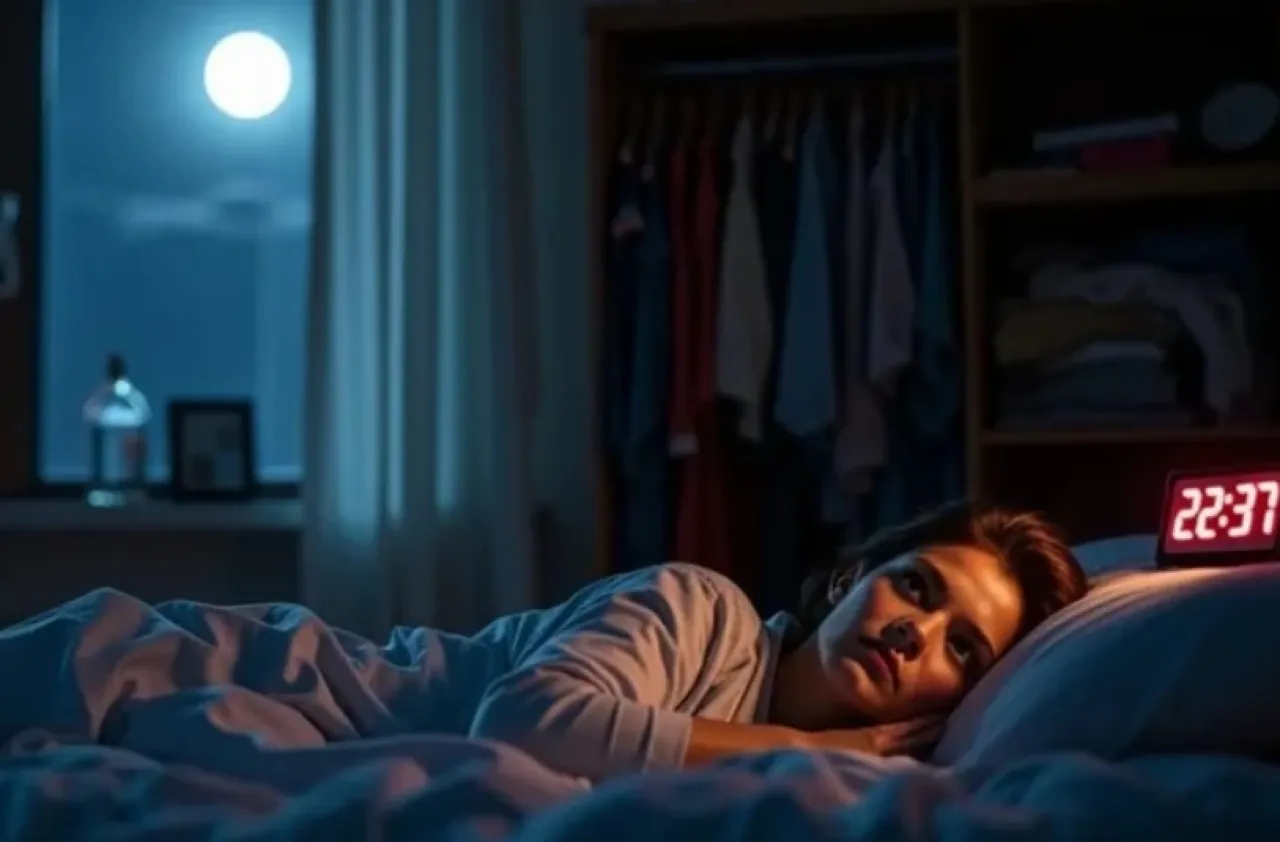
Khaberni - Sleeping for less than 7 hours per night is associated with a decrease in the expected average lifespan, according to a study that included 3 thousand counties in the United States.
The results of sleep deprivation were similar regardless of income level or accessibility to healthcare or geographical location (urban or rural), according to "Study Finds".
And sleep deprivation is the second strongest indicator of decreased expected lifespan after smoking, ahead of physical inactivity and diabetes.
According to the study conducted at the University of Oregon Health & Science, the relationship between lack of sleep and mortality rates remained consistent throughout all the years covered by the study (2019- 2025), including during the COVID-19 pandemic, and remained valid even after the researchers took into account factors such as obesity, smoking, and other major health issues.
Smoking
Smoking showed the strongest link with decreased expected average lifespan. Sleep came in second place, ahead of obesity, diabetes, and physical inactivity.
When the researchers conducted a second analysis including obesity and diabetes as additional factors, both smoking and obesity showed a stronger link with expected average lifespan than sleep deprivation. However, sleep insufficiency remained an important predictive factor even in this extended model.
These results challenge assumptions about the factors that influence lifespan at a community level. While access to health care, education, and economic opportunities are important, it seems that the amount of sleep the population gets is equally significant..