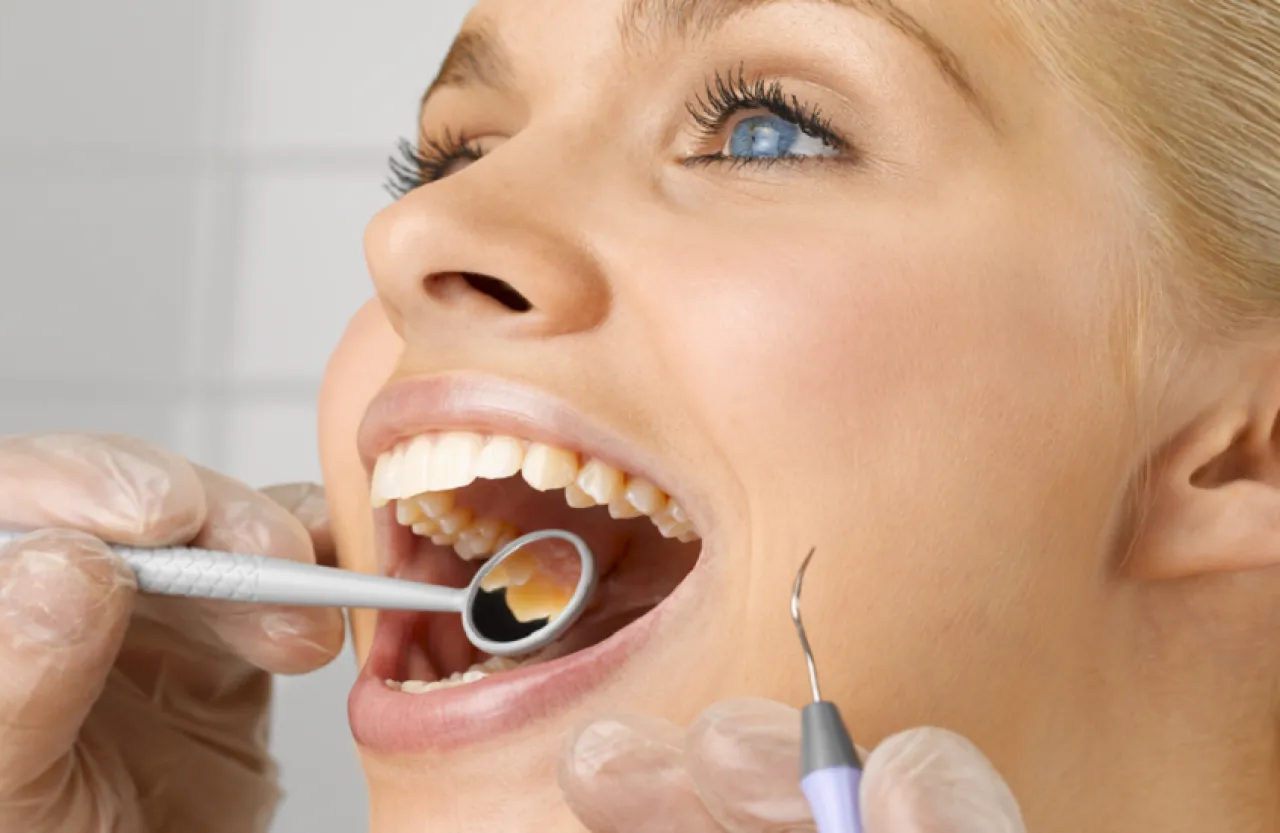
Medical care for diabetic patients usually focuses on the heart, feet, eyes, liver, and kidneys, while the mouth is often neglected despite the suffering of patients from gum pain, dry mouth, and difficulty chewing.
Studies suggest that controlling blood sugar levels and caring for oral health play a major role in improving quality of life and preventing health complications.
How does diabetes affect the mouth?
Diabetes raises blood sugar levels for long periods, which harms blood vessels and nerves, slows healing, and weakens the body's ability to fight infections.
The mouth, containing soft and hard tissues and natural bacteria, becomes more susceptible to risk. Common complications include:
Dry mouth and decreased saliva secretion.
Increased tooth decay.
Gum diseases, including inflammation and bone loss around the teeth.
Oral infections such as thrush and mouth ulcers.
Difficulty wearing dentures and altered taste.
Tooth loss in advanced cases.
These issues affect nutrition, self-confidence, and even the control of blood sugar levels. Recent studies indicate a strong relationship between type 2 diabetes and severe dental decay, due to high blood sugar and changes in the quantity and quality of saliva.
Gum Disease and Diabetes
Diabetic patients are more susceptible to gum disease; high blood sugar increases sugar levels in saliva, which feeds bacteria that produce acids irritating the gums and damaging the bones supporting the teeth, possibly leading to tooth looseness or loss.
Maintaining blood sugar levels within a healthy range, along with daily oral care, significantly reduces this risk.
Dry Mouth and Tooth Decay
About 20% of the general population suffers from dry mouth, and this percentage increases in women and the elderly. Some medications, such as blood pressure drugs, antidepressants, or nerve pain relievers, may exacerbate the problem.
Saliva protects the mouth by washing away food particles, balancing acids, and preventing infections. Without it, the mouth becomes more acidic, and the teeth lose minerals, increasing decay. Dentists can provide personalized preventive plans, such as fluoride toothpaste, specialized mouthwashes, or fluoride tooth varnish.
Saliva is also important for those wearing dentures, as it reduces irritation, secures the dentures, and lessens inflammation. When the mouth is dry, dentures may cause painful friction and mouth sores and infections like oral thrush.
Care for Dentures and Dental Implants
Dentures should be cleaned daily, removed at night, and gums and tongue should be cleaned with suitable cleaning solutions along with regular check-ups, which facilitates eating and reduces health risks.
Dental implants are an important option for replacing lost teeth, but control of diabetes must be established beforehand. High sugar levels slow healing, increase infections, and complicate bone adherence to the implant. Healthy gums, stable bones, and good oral hygiene are essential for the success of the procedure.