Khaberni - Hemorrhoids represent a common health issue that causes annoying pain and significant embarrassment for those afflicted, especially when symptoms worsen. So when does surgical treatment become the most suitable option?
The German Society for Colon and Rectal Surgery clarified that the decision to resort to surgery primarily depends on the size of the hemorrhoids and the severity of the accompanying symptoms, indicating that surgical intervention becomes necessary in advanced stages of the disease.
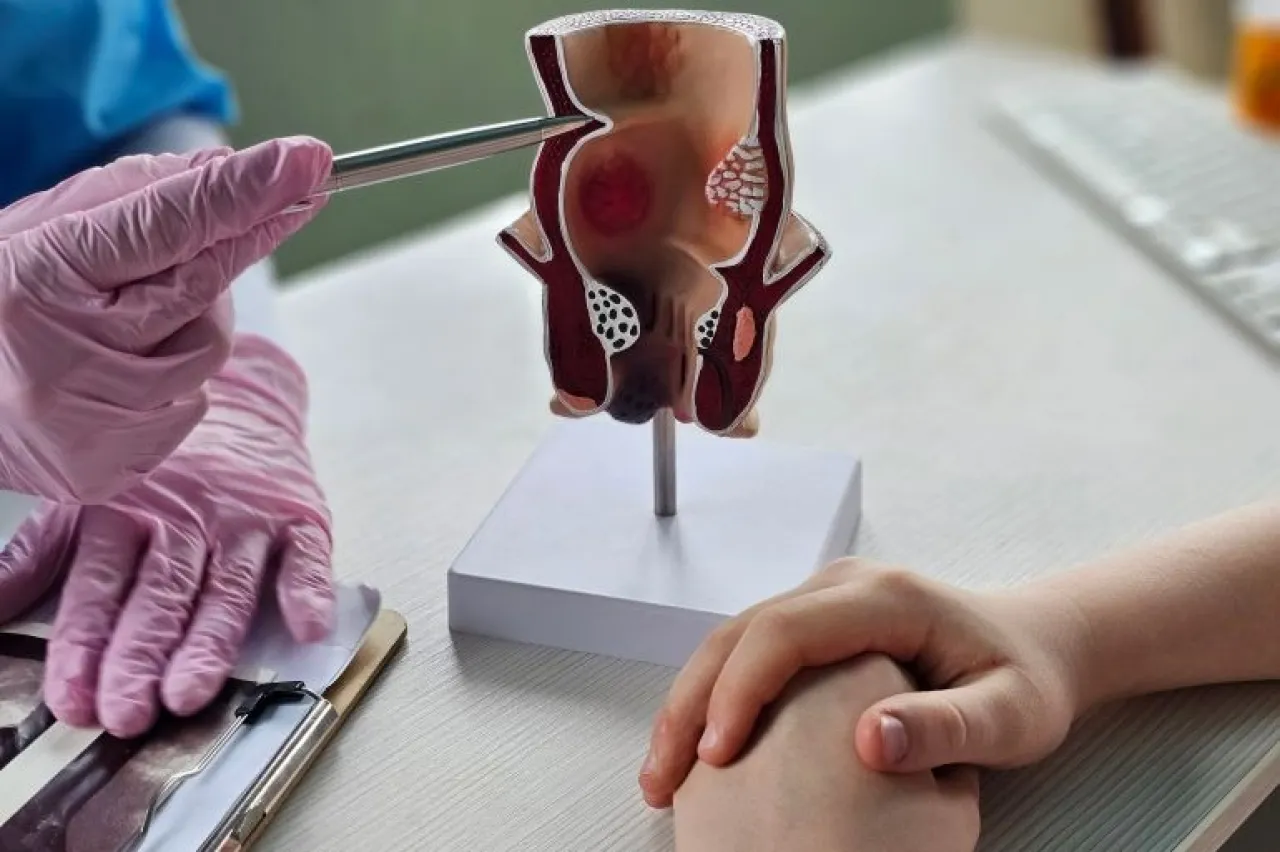
4 grades of hemorrhoids
Doctors classify hemorrhoids into 4 grades, and surgery is usually required at grade 3 or 4. These stages are characterized by the protrusion of the hemorrhoids outside the anal opening during defecation or physical exertion, without spontaneously retracting.
The symptoms in these stages are more severe and frequent, causing clear suffering for the patient, which makes surgery a direct treatment option without the need to try other therapeutic means.
When should surgery be postponed?
Before deciding on surgery, doctors emphasize the necessity of evaluating the patient’s overall health condition, as some factors may pose an increased risk during the operation, necessitating its postponement or avoidance.
Potential contraindications for surgical intervention
The conditions that may contradict hemorrhoid surgery include:
Suffering from chronic inflammatory bowel diseases
Inherited or acquired immune deficiencies
Severe metabolic disorders
Increased risk of bleeding, especially among those taking medications that prevent platelet clumping
Generally, hemorrhoid surgery is not advised during pregnancy, even in severe cases, as conservative treatments are preferred first, and surgery is only performed if these methods fail.
Postoperative care
After hemorrhoid surgery, the patient needs close medical follow-up to promote wound healing and alleviate symptoms.
Minor bleeding, wound secretion, the sensation of a foreign body, in addition to pain, are common symptoms during the first 4 weeks after the operation.
To alleviate pain, the use of pain relievers such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen, along with topical ointments containing glyceryl trinitrate or calcium channel blockers, is advisable, which significantly reduce pain.
Maintaining soft stools to avoid pain during defecation may require the use of short-term laxatives, in addition to increasing fluid intake and eating fibers such as psyllium husks.
Doctors confirm that good pain control accelerates recovery and facilitates the return to daily life after hemorrhoid surgery.