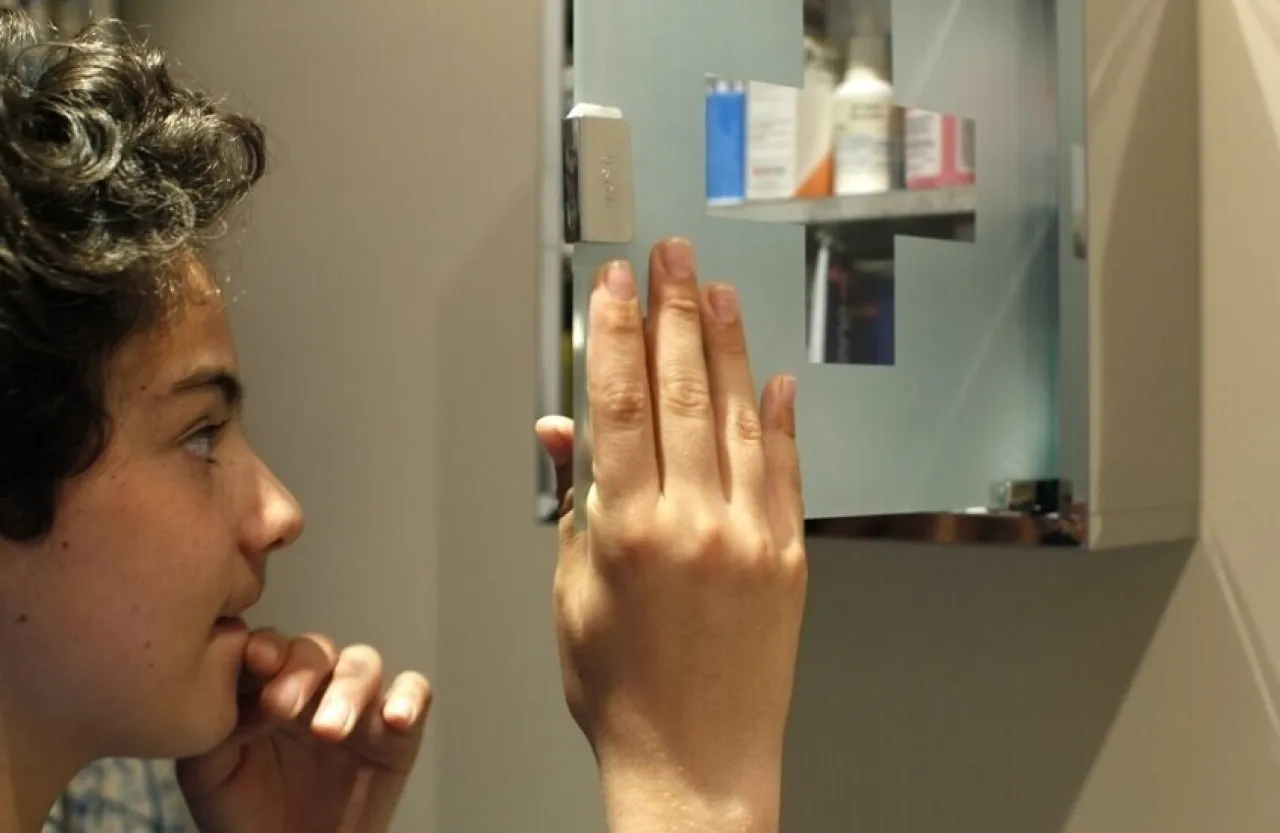
Khaberni - Associate Professor Alexei Panov from the Russian Technical University reported that the common belief that the refrigerator is the ideal and safest place to store household medicines is completely wrong.
He explained, "For a number of medications, cooling, especially freezing, does not improve their storage, but may lead to the loss of their therapeutic properties and the formation of dangerous decomposition products. Therefore, the storage conditions for each medication are separately determined by the manufacturing company and mentioned in the user instructions."
He added that the main danger of the refrigerator, aside from the possibility of freezing, lies in the combination of low temperatures and high humidity. Some dosage forms like tablets, powders, capsules, and some ointments are highly sensitive to moisture, and when stored in inappropriate conditions like a regular refrigerator compartment without airtight container, they may be exposed to moisture, which can lead to changes in their physical and chemical properties, damage to active components, as well as the risk of microbial growth. This applies especially to herbal preparations and products made from natural ingredients.
Dr. Panov mentioned that there are medications that should never be frozen, including most vaccines, insulin, some types of interferon, and other protein-based medications. He said, "The active ingredients in these medications, such as proteins and fats, are susceptible to damage at temperatures below zero. This irreversible change in the molecular structure renders the medication useless, and in the case of vaccines, the drug loses its immunological properties. Freezing may also cause irreversible separation of emulsions or damage the ampoules. Even if the medication appears normal after thawing, its effectiveness is not guaranteed, making its use unsafe."
He added that medications in the form of syrup or aqueous suspensions should not be kept in the refrigerator unless otherwise directed by the instructions, explaining: "Often, low temperatures lead to the crystallization and precipitation of sugars and other components, making accurate dosing impossible. Liquid extracts and tinctures may become cloudy and their properties altered. Likewise, medications should not be stored near strong-smelling or moist foods such as vegetables, fruits, and fish, as this negatively affects their quality."
Dr. Panov concluded by saying: "If the medication's instructions indicate that it should be stored in the refrigerator, it should be placed in a separate, airtight container on the middle shelf, away from the freezer and door, where the largest temperature fluctuations occur."