Khaberni - Heart attacks have become one of the leading causes of death globally, and arterial blockage is the most common reason behind these medical emergencies.
According to the World Health Organization, cardiovascular diseases account for about 17.9 million deaths annually, with four out of every five deaths due to heart attacks and strokes.
In this context, Dr. Sorab Gonga explains that early diagnosis of arterial blockage is the most important factor in preventing deadly complications, especially cases associated with arteriosclerosis.
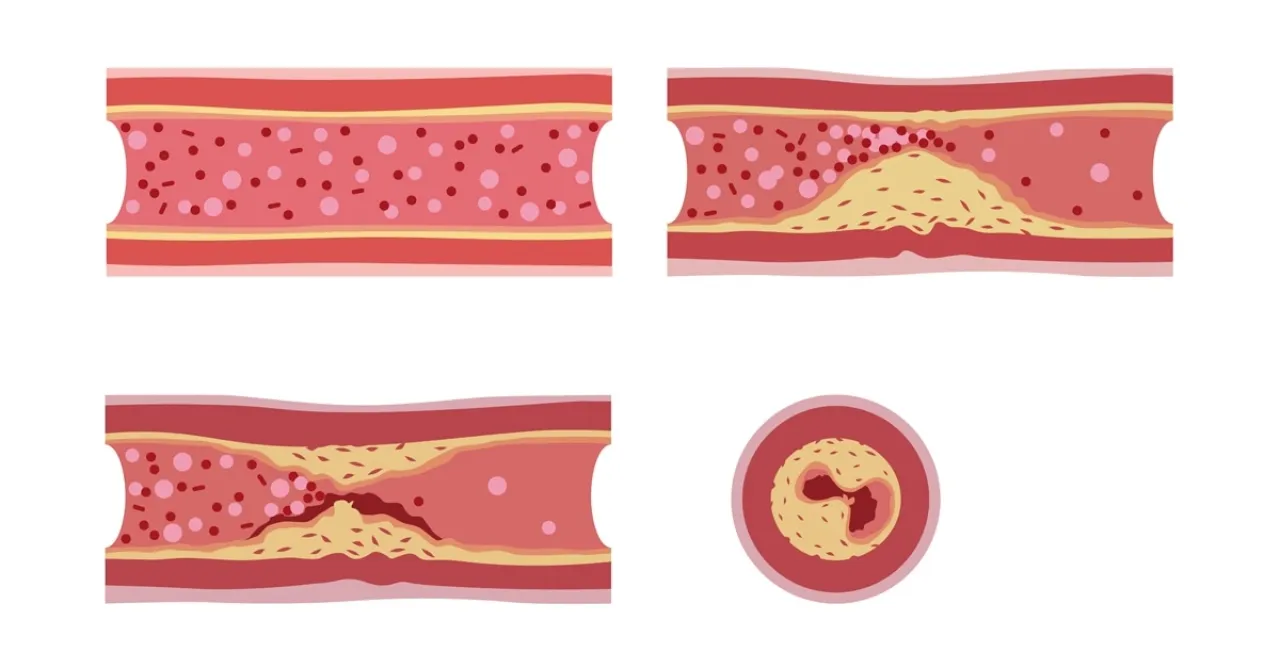
Arteriosclerosis.. A Silent Enemy
Arteriosclerosis is defined as a chronic condition where fatty plaques build up on the walls of arteries, narrowing or blocking them and limiting blood flow to vital body organs.
Dr. Gonga points to the website "Health Shots," stating that the early stages are often silent, showing no symptoms until the damage reaches an advanced stage.
Risk Factors and Most Vulnerable Groups
Dr. Gonga identified key risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing arteriosclerosis, which include:
High blood pressure
High levels of harmful cholesterol (LDL)
Smoking
Diabetes
Obesity and lack of physical activity
Unhealthy diet
Studies have also indicated that some groups are more vulnerable, including those with metabolic conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, smokers who accelerate plaque accumulation in the arteries, people older than 45 for men and 55 for women, individuals with a strong family history of heart diseases or stroke, and those suffering from chronic inflammatory conditions such as chronic kidney disease or certain autoimmune diseases.
Regular Screenings for Early Detection
Due to the difficulty in detecting arteriosclerosis in its early stages, Dr. Gonga recommends regular screenings, especially for people with risk factors, family history, or those over the age of 40. These include:
-Blood tests: measuring cholesterol, blood sugar, and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels.
-Regular blood pressure monitoring.
-Ankle-brachial index (ABI): comparing blood pressure in the ankle with the arm.
-Ultrasound imaging of the carotid artery: to detect plaque accumulation in the neck arteries.
-Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) score: measuring calcium deposits in the coronary arteries.
-Stress tests on a treadmill/ stress echocardiography: to assess heart performance and detect unseen blockages when at rest.