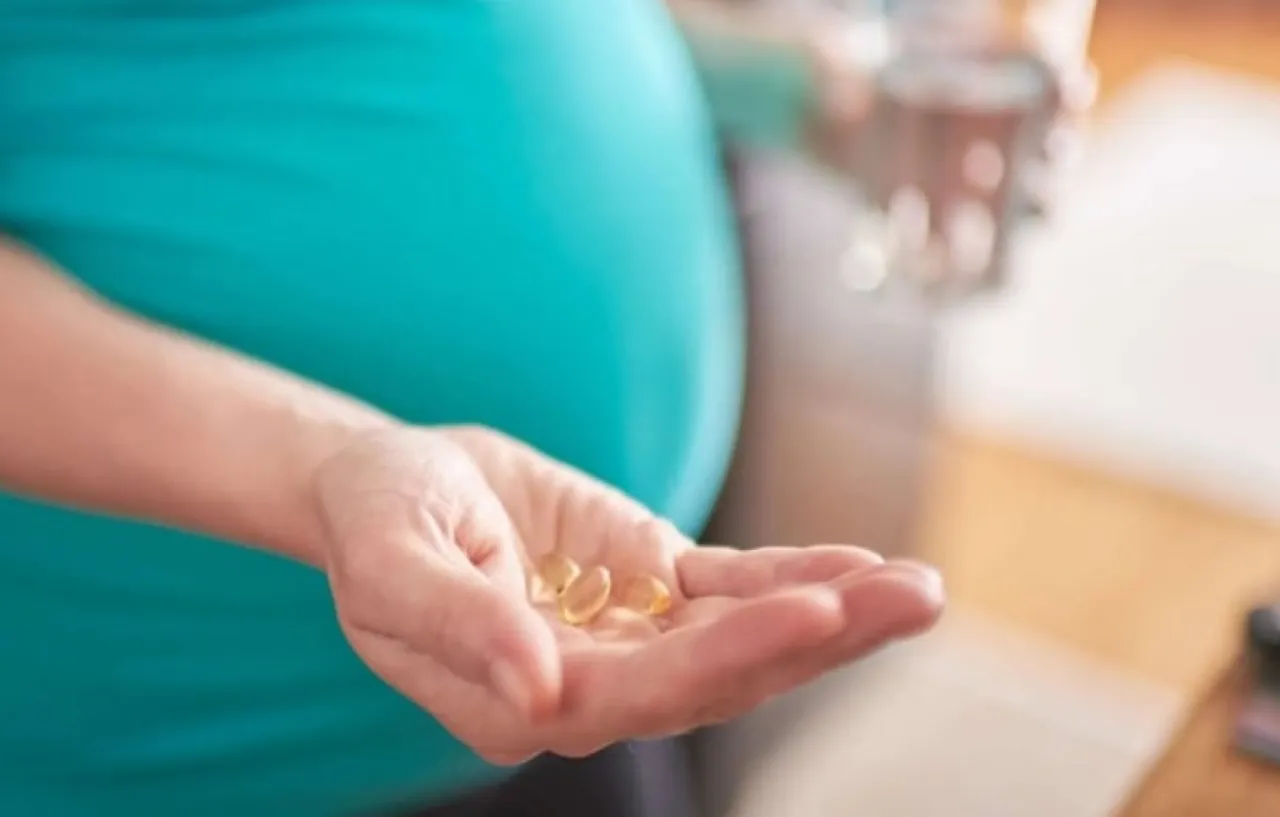
Khaberni - Researchers from Curtin University in Australia and various universities in Ethiopia reported that the intake of folic acid and multivitamin supplements before birth is associated with a 30% reduction in the risk of developing an autism spectrum disorder in children.
Previous studies have found that both genetic mutations and environmental effects contribute to the risk of developing autism spectrum disorders, where maternal nutrition before birth has been identified as a modifiable environmental factor.
Within this broader category of maternal nutrition before birth, folic acid and multivitamin supplements are among the most available interventions for women before and during pregnancy.
Folic Acid
Folic acid supports DNA and genetic regulation that shapes neurological development and supports the formation of the neural tube, processes associated with the structural growth of the brain.
According to "Medical Express", the research team in their new study reviewed 101 primary studies involving more than 3 million mothers and children.
The pooled analysis in the comprehensive review indicated that the mother's intake of folic acid and/or multivitamin supplements before birth was associated with a 30% reduction in the risk of developing autism spectrum disorders in offspring.
Results of Multiple Pregnancy Vitamins
The subgroup analysis by type of supplement found that the intake of multivitamin supplements before birth was associated with a 34% reduction in the risk of developing autism spectrum disorders. The intake of folic acid alone was associated with a 30% reduction in risk.
Multivitamin supplements typically provide vitamin B12, vitamin D, iodine, and other micronutrients that help maintain the immune balance, modulate inflammation, and support the synthesis of neurotransmitters and metabolism of amino acids, creating a nutritional environment that promotes optimal brain development of the fetus and possibly reduces the risk of developing autism spectrum disorders.
Global estimates in the reviewed materials suggest that the prevalence of autism spectrum disorders reaches 1% in children.
Autism spectrum disorder affects mutual social interaction, non-verbal communication, and understanding of social relationships.