Khaberni - In a promising medical achievement, researchers in the UK have developed a new artificial intelligence tool capable of analyzing blood cell abnormalities with accuracy surpassing hematology experts.
The tool, named "Cellular Diffusion Model," could revolutionize the diagnosis of serious diseases such as leukemia, and relies on the same generative artificial intelligence techniques used in AI models for generating images from text like "DALL-E," but it is specialized to monitor the finest differences in the shape and structure of blood cells.
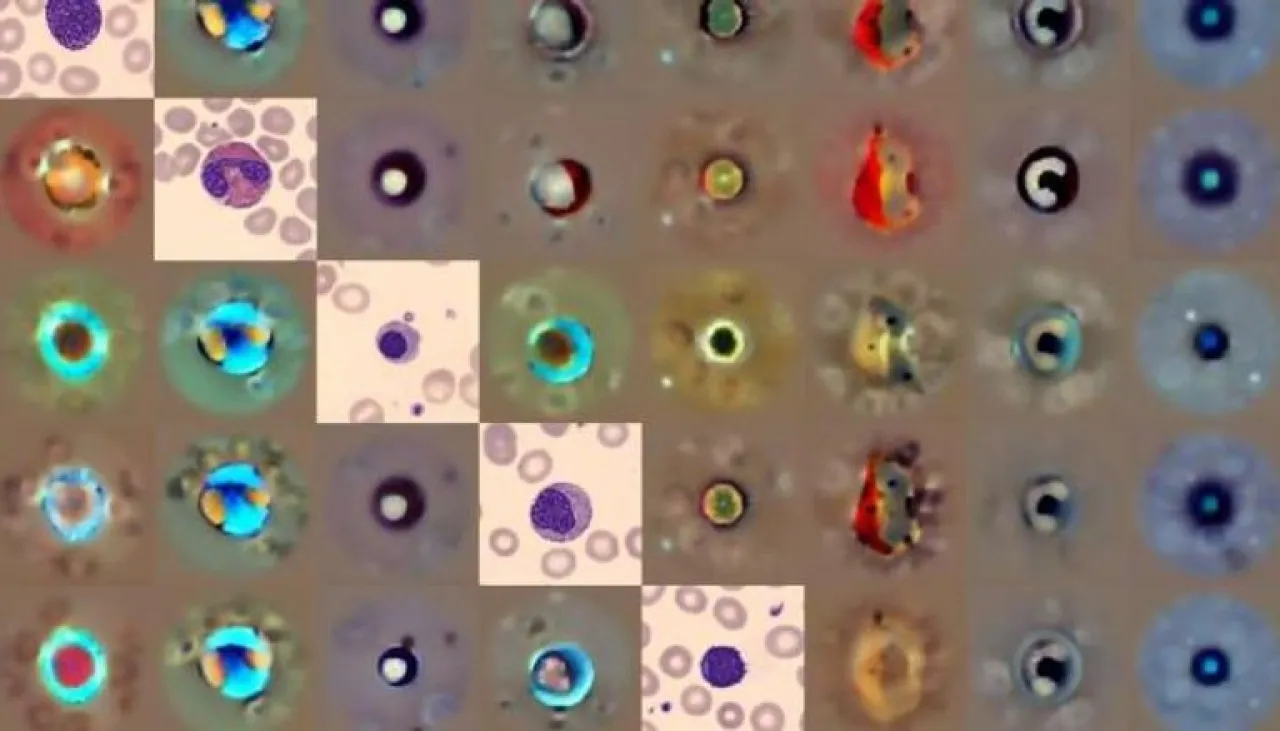
Different types of blood cells were analyzed using the "Cellular Diffusion Model" tool
The study, published in the journal "Nature Machine Intelligence," reveals that the system can distinguish between thousands of cells in a single "blood smear," identifying normal, abnormal, and even rare cells, a task that can take a long time for a doctor and sometimes leads to different assessments among experts.
A technology that looks beyond human sight
Researcher Simon Deltadhal from the University of Cambridge, the lead author of the study, says that the major advantage of the tool lies in its ability to scan thousands of cells at once, which is "impossible for humans." He added, "Our model can automatically sort routine cases and highlight any abnormal cell for doctor review."
The drive behind developing this tool was a personal experience of a young hematologist involved in the research, Dr. Sotish Sevapalaratnam, who said: "After a long day at work, I was facing many blood slides to analyze. I was convinced that artificial intelligence could perform the task with greater precision."
The researchers trained the model on more than 500,000 images from Addenbrooke's Hospital in Cambridge, the largest collection of blood smear images (blood samples spread on a glass slide for microscopic examination) collected for research purposes, including common and rare cells, as well as elements that could confuse automated systems.
Unlike traditional models that categorize cells into specific categories, the innovative "Cellular Diffusion Model" represents the full shape of cell diversity, making it more capable of dealing with differences in imaging devices and microscopes, detecting unfamiliar cells, and recognizing abnormalities associated with leukemia with higher sensitivity than current systems.
The tool not only outperformed doctors but also excelled in determining the level of uncertainty in its decisions, a fundamentally human skill.
Artificial intelligence deceives doctors
In a striking step, the model produced synthetic images of blood cells identical to real images. When shown to 10 hematologists, they could not distinguish them from the actual images.
Deltadhal said: "This was astonishing.. These experts look at blood cells all day, yet they could not differentiate."
Different types of blood cells were analyzed using the "Cellular Diffusion Model" tool
The researchers are also launching the world's largest public database of blood smear images, over half a million images, to enable researchers around the world to develop new models that enhance the diagnosis of blood diseases.
The team emphasizes that the innovative "Cellular Diffusion Model" will not replace doctors, but it will create a significant shift in the speed and accuracy of diagnosis.
Professor Parashkev Nashiyev from University College London comments, saying: "The real value of artificial intelligence lies not in imitating experts, but in its ability to offer diagnostic and predictive power beyond what humans or traditional statistics can achieve."
The researchers are now studying developing the model to become faster and more capable of dealing with patient variations around the world to ensure accuracy and equity in diagnosis.