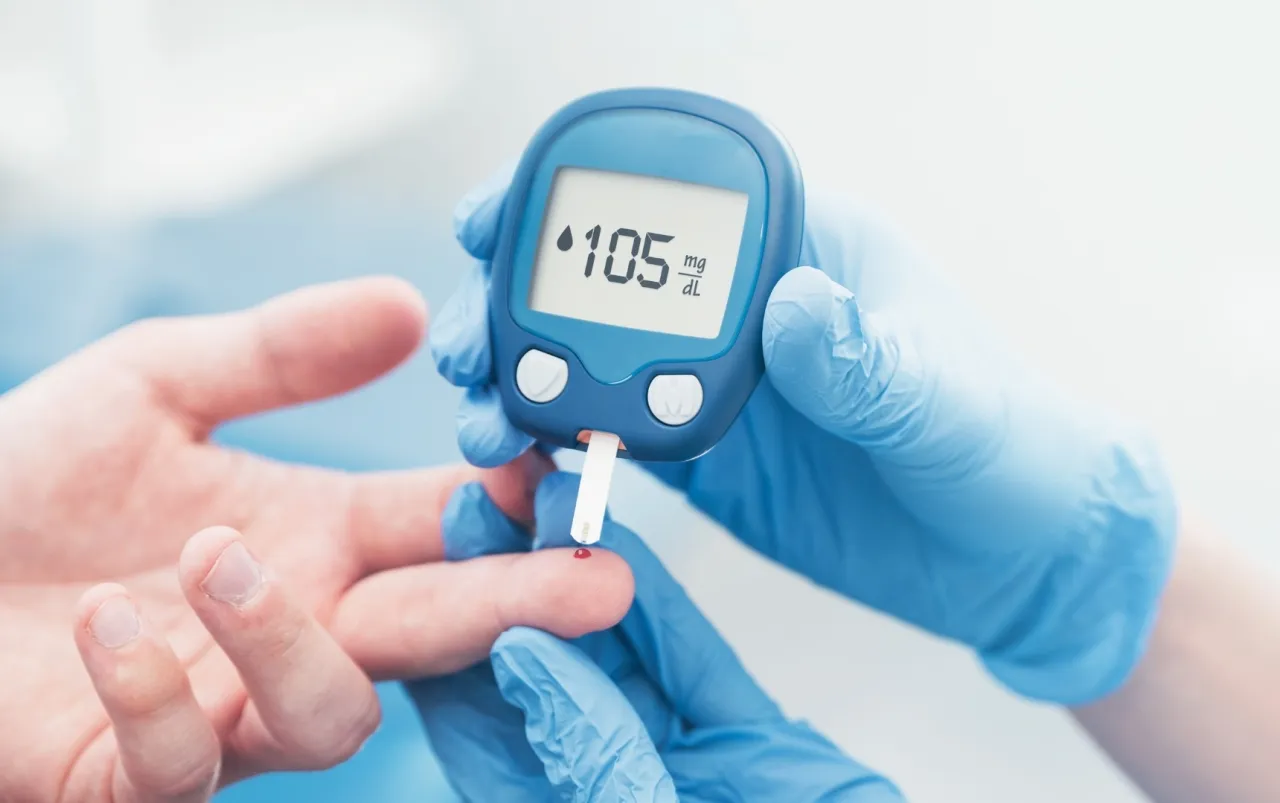
Khaberni - Type 1 diabetes is a medical condition arising from the failure of beta cells in the pancreas to secrete enough insulin, with an estimated 9.5 million people affected worldwide.
This decrease in insulin levels causes glucose levels to remain high in the blood, which can cause long-term damage to organs such as the kidneys, eyes, and cardiovascular system.
Diabetes patients require lifelong continuous monitoring of blood sugar levels, along with insulin injections to maintain stable sugar levels within healthy ranges.
One of the new potential treatment options for these patients is to replace damaged or non-functioning beta cells, either through cell transplantation or by generating new beta cells from existing cells within the body.
This latter approach was followed by the team of Xiaofeng Huang from Weill Cornell Medical College in the United States and Qing Xia from Peking University in China, who previously discovered the possibility of converting mouse stomach cells into pancreatic beta cells through genetic engineering.
In the research published in the journal Stem Cell Reports, the researchers tested whether the same result could be achieved with the human stomach inside the body.
To test this, the researchers began by creating human intestinal organoids (microscopic structures that simulate aspects of normal stomach functions), then genetically modified these organoids so they could be converted into pancreatic beta cells when a genetic switch is activated.
Subsequently, the gastrointestinal organoids were implanted in the abdominal area of mice, where they survived and matured for up to six months, forming connections with surrounding tissues and the blood system. When the genetic switch was activated, the human stomach cells transformed into insulin-producing cells within the mice, and they resembled pancreatic beta cells in terms of gene expression and protein characteristics.
Encouragingly, when these experiments were conducted on diabetic mice, the insulin secreted by the transformed human cells helped control blood sugar levels and improve the diabetic condition.
The scientists hope that a similar approach could be applied to convert cells from a patient's own stomach into insulin-producing cells directly within the body. However, it is important to note that further studies are needed.